Not all people are aware of what hyperpigmentation is and plenty of those who know have wrong beliefs on how to treat it.
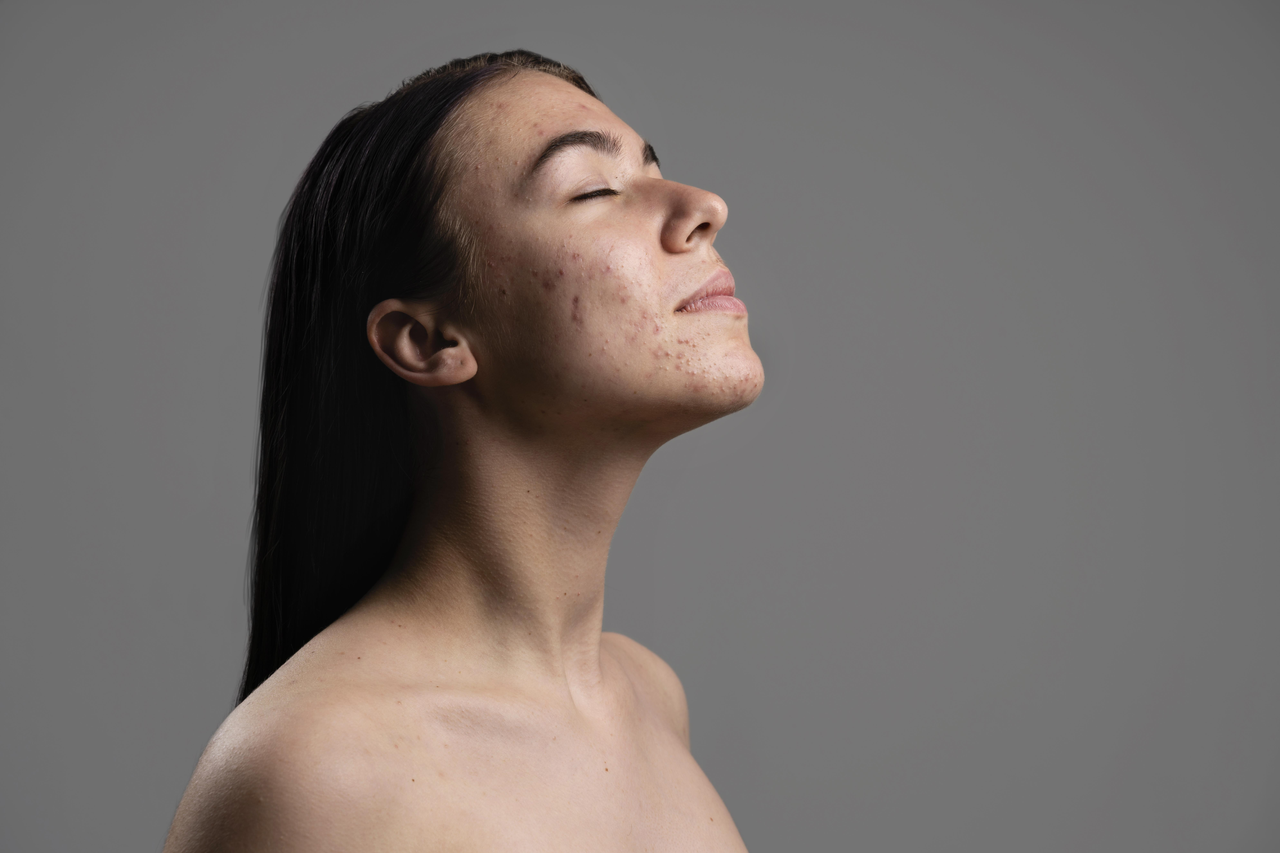
Let’s set the record straight. Hyperpigmentation is a condition that causes patches of skin to become darker in color than the surrounding skin. This can affect any part of the body, but it’s most commonly seen on the face, hands, and arms.
While the cause of hyperpigmentation is not fully understood, there are many myths and misconceptions about the condition. Many people aren’t aware of the truth and this lack of knowledge can often lead to confusion and frustration when attempting to treat their dark spots.

In this article, we will explore some of the most common myths about hyperpigmentation, as well as the facts that disprove them.
Myth: All dark patches on the skin are hyperpigmentation.
Fact: Not all dark patches on the skin are caused by hyperpigmentation. Some of them may be due to other skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis. Hyperpigmentation can also be side effects of diseases like hyperthyroidism, Addison's disease, or hemochromatosis.
Myth: All types of hyperpigmentation are the same.
Fact: There are several different types of hyperpigmentation, including melasma, freckles (ephelides), solar lentigines, age spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Each type has its own unique characteristics and causes.
Myth: Hyperpigmentation is always caused by too much sun exposure.
Fact: While sun exposure is one of the main causes of hyperpigmentation and can worsen existing dark spots, there are many other factors that can contribute to the condition. These include hormonal changes, aging, genetics, pregnancy, acne, autoimmune diseases, birth control pills, and certain medications.
Myth: Sunscreen causes skin hyperpigmentation.
Fact: Sunscreen does not cause skin hyperpigmentation. It’s actually an important part of a comprehensive skin care regimen for people with hyperpigmentation because it can prevent further sun damage which can cause dark patches to become even darker. Sunscreen protects your skin against the sun’s UV rays so choose a sunscreen that is labeled “broad spectrum” and has an SPF of 30 or higher.
Myth: Sunscreen will always prevent hyperpigmentation from occurring.
Fact: Sunscreen is an important part of any treatment plan for hyperpigmentation, but it cannot stop hyperpigmentation from happening entirely. As there are plenty other causes of this skin condition aside from sun exposure, sunscreen can’t be the all-in-one answer to its prevention.
Myth: Hyperpigmentation is a rare condition.
Fact: Hyperpigmentation is actually a very common condition. All people experience some kind of hyperpigmentation at some point of their lives. May this be because of melasma from pregnancy, acne marks, scarring, or a shift in hormones.
Myth: Hyperpigmentation is permanent.
Fact: This is not always true. The majority of cases of hyperpigmentation are temporary and will fade over time with proper treatment. An example of this is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which is a form of hyperpigmentation that’s reversible. Many dark spots may disappear on their own while others can be removed through prescriptions and skin products. However, there are also some kinds of hyperpigmentation that are permanent unless cured with surgery or other technological treatments.
Myth: Skin hyperpigmentation is a serious health condition and is always a sign of bad health.
Fact: Hyperpigmentation is not necessarily a premonition to diseases and health problems. It’s simply a common skin condition that causes areas of the skin to become darker than the surrounding skin. Although hyperpigmentation can be unsightly, it is usually benign and harmless. Only be alarmed if your dark spots have accompanying pain, irritation, swelling, and itchiness. If you experience these other symptoms along with your hyperpigmentation, it can be a sign of another disease or skin problem.
Myth: Hyperpigmentation is a sign of cancer.
Fact: Hyperpigmentation doesn’t normally imply cancer. While it’s important to have any abnormal lesions or moles checked by a doctor, hyperpigmentation isn’t a typical cancer symptom. On the other hand, a type of skin cancer called melanoma does have hyperpigmentation as its indication. Nonetheless, this kind of hyperpigmentation is different as it usually comes with moles and unusual growth. If your hyperpigmentation doesn’t look unnatural and abnormal, you have nothing to worry about.
Myth: Hyperpigmented patches are contagious.
Fact: Hyperpigmentation isn’t a disease and it definitely isn’t contagious. One dark spot doesn’t spread and multiply across your skin. Neither does it transfer to another person upon contact. There are two types of hyperpigmentation: primary and secondary. Primary hyperpigmentation occurs when melanin is overproduced in certain areas of the skin, while secondary hyperpigmentation develops as a result of another skin condition or injury. Hyperpigmentation doesn’t develop because of transmission.
Myth: Only people with light skin get hyperpigmentation.
Fact: People of all skin colors can get hyperpigmentation. The condition can affect anyone, regardless of race or ethnicity. Contrary to popular belief, people with darker skin tones are actually more prone to hyperpigmentation than those with fairer complexions.
Myth: Only women get hyperpigmentation.
Fact: Men can also get hyperpigmentation. It is not just a problem for women. This stereotype came to be because women are more conscious than men when it comes to blemishes so they’re the ones usually looking for ways to make hyperpigmentation disappear. Most men don’t share this sentiment as they’re not pressured with this kind of “beauty standard” unless their hyperpigmentation is very obvious and widespread on the skin. Both men and women experience dark patches and both should also be given the same options for treatment.
Myth: Hyperpigmentation is a sign of poor hygiene or that it can be cured with bleach or other harsh chemicals.
Fact: Bad hygiene isn’t a cause of hyperpigmentation and the condition will only worsen when you put harsh chemicals on your skin under the mistaken belief that these could make the dark spots fade. Bleach and chemicals will only irritate your skin. Hyperpigmentation isn’t “dirty” so it doesn’t need cleaning. What it needs is a gentle treatment that can naturally induce the skin to shed off the dark skin cells and produce fresh brighter cells.
Myth: You can't do anything to treat hyperpigmentation.
Fact: There are many treatments available for hyperpigmentation. You can get rid of your dark patches with a variety of methods, including topical medications, laser treatments, surgery, and chemical peels. Some of these cost more than others so choose an affordable and effective treatment for you.
Myth: Hyperpigmentation can only be treated with prescription medications or surgery.
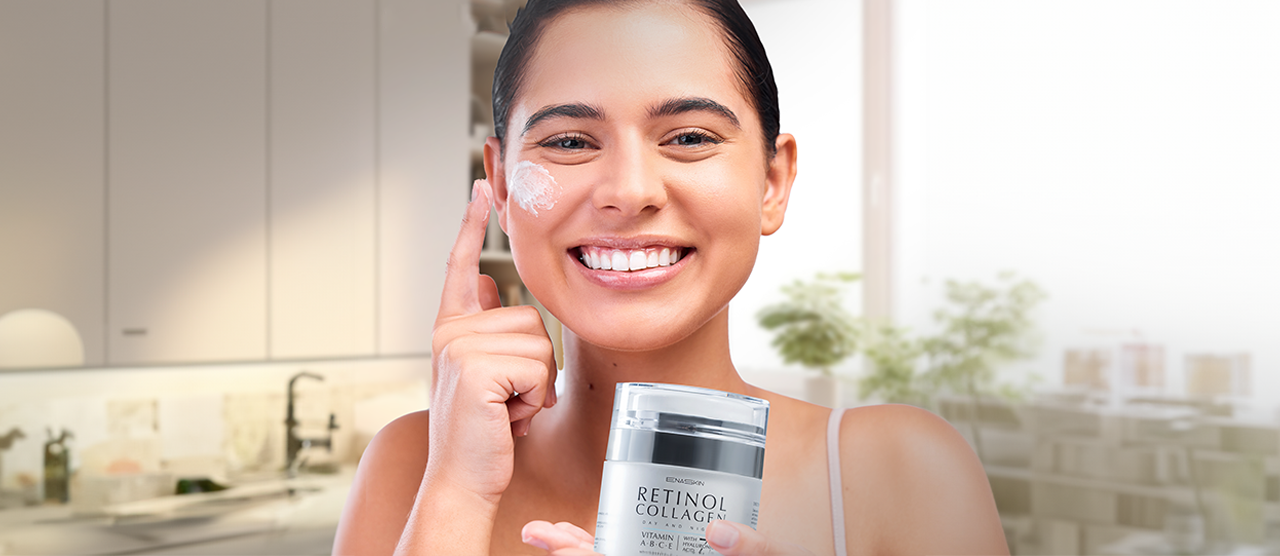
Fact: There are many treatments available for hyperpigmentation that don't require medication or surgery. If you don’t like swallowing tablets or having surgical tools cutting into your flesh, then you can choose products that you can simply apply on your skin like the EnaSkin Dark Spot Corrector, which removes dark spots without any risk and pain.